Diabetes is a chronic condition that can lead to a number of complications. It affects more than one-quarter of American seniors. According to a worrying statistic about 10 to 15 percent people with diabetes are afflicted with foot and leg ulcers. If untreated and untreated, these seemingly harmless injuries can become serious and result in diabetic foot amputation. In fact, over 80 percent of all amputations stem from foot ulcers, highlighting the necessity of taking care to provide prevention and care.
Diabetes management is a difficult issue that requires a holistic method that goes far beyond glucose control. The daily foot care routine is the keystone in this effort that serves as the primary protection against the imminent threat of amputations due to diabetes.
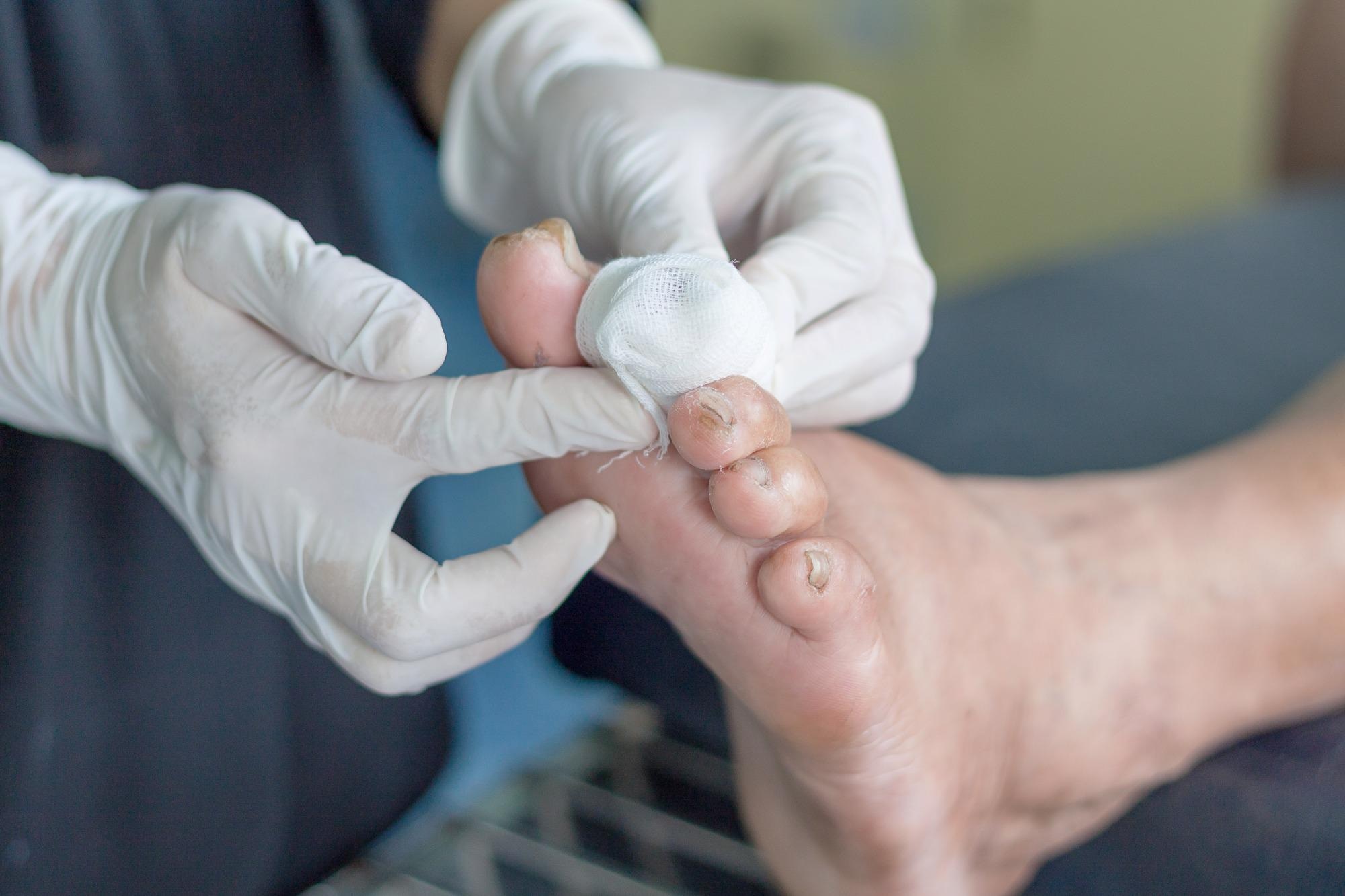
Understanding the Landscape
The world of diabetes and its complications is a complex one. Patients with diabetes are more likely to develop leg and foot ulcers. This emphasizes the importance of proactive care and greater awareness. The data is stark and it is clear that understanding these complexities will be crucial to fight against the amputation.
The Amputation Conundrum
The possibility of an amputation is always in the forefront of diabetics. It’s much more than a statistic. It impacts individuals directly. It’s an extended journey from a minor injury up to the possibility that you may need amputation due to diabetes.
Daily Foot Care: A Shield From Amputation
The foundation of diabetes amputation prevention lies in daily foot care. It’s not just an everyday foot care routine. It’s also a methodical procedure to detect and resolve possible issues before the issue escalates. From checking feet for injuries to ensuring the proper moisturization of your feet, every step of this routine is a crucial step in the battle against diabetes-related amputations.
The Role of Vascular Specialists
Vascular specialists don’t deal with diabetes in a direct manner, however their expertise is vital in managing complications. To alleviate discomfort in the legs and to speed up wound healing, creating optimal blood flow is an essential element of treatment. The goal of this collaborative strategy is to prevent Amputations due to diabetes by minimizing its effects.
Amputation Prevention: Strategies
A blend of vigilance, alertness and expert guidance is essential to navigate through the confusing world of diabetes-related amputations. For individuals grappling with diabetes, adopting an active attitude is crucial. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers and vascular specialists can aid in early detection and treatment.
Leg Ulcers and Beyond Leg Ulcers: Triggers to Think About
The leg ulcers, frequently the precursors to more serious complications, need attention and knowledge. Understanding the causes that lead to leg ulcers can be a critical step. The cause could be poor circulation, neuropathy or a combination of causes, identifying the root cause allows for targeted interventions and customized treatment.
Education as empowerment
It is essential to educate those with diabetes on the risks of the disease and how to stop these risks. Educational initiatives in healthcare settings as well as the broader public can help bridge the gap in awareness. Knowing the consequences of injuries that appear harmless can result in timely interventions and possibly averting the necessity for diabetic feet amputation.
Private battles, collective triumphs
Amputations related to diabetes is not solely an individual battle; it’s a global victory. Joining support groups through your doctor or in the local community is a good way to share experiences to gain knowledge and develop coping techniques. The possibility of losing limbs can be emotional draining. The feeling of belonging is a fantastic way to find strength and comfort.
Conclusion: The process of battling ulcers, diabetes, and the possibility of an amputation is multi-faceted. Daily foot care stands as the first line of defense. Likewise, the skills of vascular specialists become vital in reducing the effects. Diabetes patients can reduce the possibility of losing a foot through educating themselves, taking prevention measures and creating an underlying support system.